Decision Tree is a type of supervised learning algorithm that is mostly used for classification problems. This works for both categorical and continous dependent variables.
A decision tree is a graphical representation of all the possible solutions to a decision based on certain conditions.
What is Classification?
Classification is the process of dividing the datasets into different categories of groups by adding labels.
Types of classification -
- Decision Tree
- Random Forest
- Naive Bayes
- KNN
Dataset
We will be using a simple dataset to implement this algorithm. This dataset contains details of patient like Age, Sex, BP, Na_to_K and Drug column. Drug column has data as drugX, drugY, drugA, drugB and drugC. Using Decision Tree we will predict what drug to be given to the patient.
Download the dataset here.
So let’s begin here…
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.externals.six import StringIO
import pydotplus
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
%matplotlib inline
Load Data
data = pd.read_csv('drug200.csv')
data.head()
| Age | Sex | BP | Cholesterol | Na_to_K | Drug | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 23 | F | HIGH | HIGH | 25.355 | drugY |
| 1 | 47 | M | LOW | HIGH | 13.093 | drugC |
| 2 | 47 | M | LOW | HIGH | 10.114 | drugC |
| 3 | 28 | F | NORMAL | HIGH | 7.798 | drugX |
| 4 | 61 | F | LOW | HIGH | 18.043 | drugY |
Dependent and Independent variables
X = data[['Age','Sex','BP','Cholesterol','Na_to_K']].values
y = data[['Drug']].values # Dependent variable
le_sex = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
le_sex.fit(['F','M'])
X[:,1] = le_sex.transform(X[:,1])
le_BP = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
le_BP.fit(['LOW','NORMAL','HIGH'])
X[:,2] = le_BP.transform(X[:,2])
le_Chol = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
le_Chol.fit([ 'NORMAL', 'HIGH'])
X[:,3] = le_Chol.transform(X[:,3])
Train and Test data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
Define Model
model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy", max_depth = 4)
Fit Model
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='entropy', max_depth=4,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False, random_state=None,
splitter='best')
Prediction
predTree = model.predict(X_test)
Accuracy
print("Decision Trees's Accuracy: ", metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, predTree))
Decision Trees’s Accuracy: 0.9666666666666667
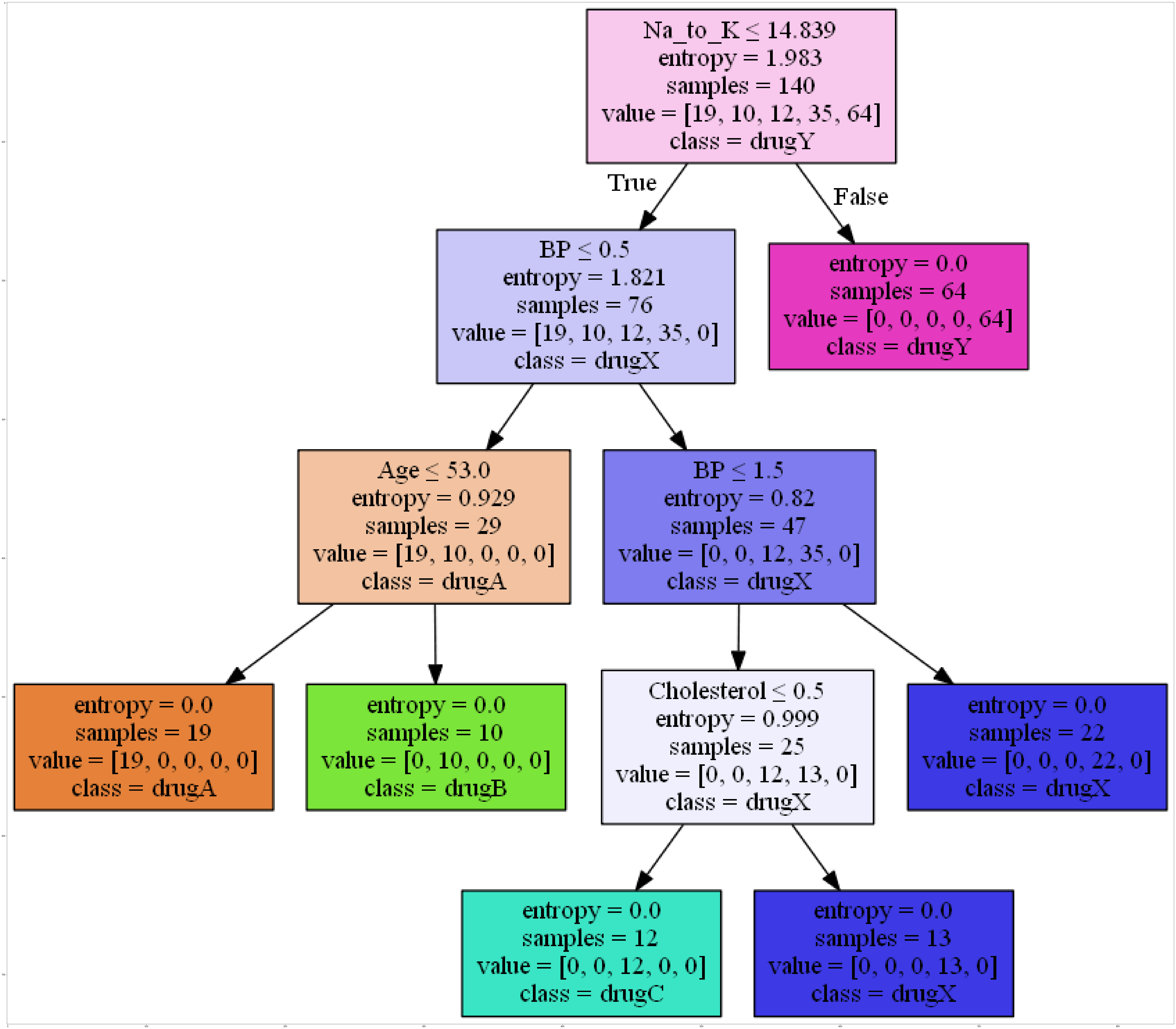
Decision Tree
dot_data = StringIO()
filename = "drugtree.png"
featureNames = data.columns[0:5]
targetNames = data["Drug"].unique().tolist()
out=tree.export_graphviz(model,feature_names=featureNames, out_file=dot_data, class_names= np.unique(y_train), filled=True, special_characters=True,rotate=False)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data.getvalue())
graph.write_png(filename)
img = mpimg.imread(filename)
plt.figure(figsize=(100, 200))
plt.imshow(img,interpolation='nearest')
If the relationship between dependent and independent variable is well approximated by a linear model then linear regression will outperform tree based model.
If there is high non linearity and complex relationship between dependent and independent variables a tree model will outperform a classical regression model.